In the spirit of recognising that there are many different ways to pick stocks, a year ago I wrote an article, Stock market winners versus losers, on using a basic momentum strategy to select stocks. The premise went as follows: academic researchers have found that portfolios of recent outperformers did better than portfolios of recent underperformers. So a long short strategy constructed this way should generate a positive return. We tested this approach in the Australian marketplace and found what appears to be a volatile but high performing strategy. How did this strategy perform in the most recent financial year?
2014-15 financial year performance
A brief refresher on the strategy:
- At the start of each financial year we hypothetically go long an equally weighted portfolio of the previous financial year’s top 10 performing stocks on the ASX 200
- We hypothetically also short an equally weighted portfolio of the previous financial year’s worst 10 performing stocks on the ASX 200
- This portfolio is held untouched for the subsequent financial year (i.e. a 12 month holding period).
The table below lists stocks we would have held, long and short, during the previous financial year (2014 / 2015), based on their performance over the previous 12 months, along with their subsequent performance.
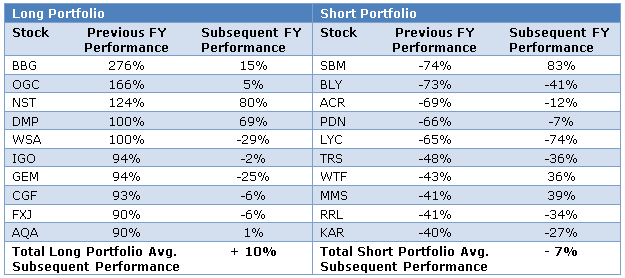
Using the table, if we subtract the short performance (-7%) from the long performance (+10%) we end up with a total performance of 17%. The last financial year has been another solid year of performance for this strategy; a little less than the long term average. The chart below presents the updated track record (now 11 years).
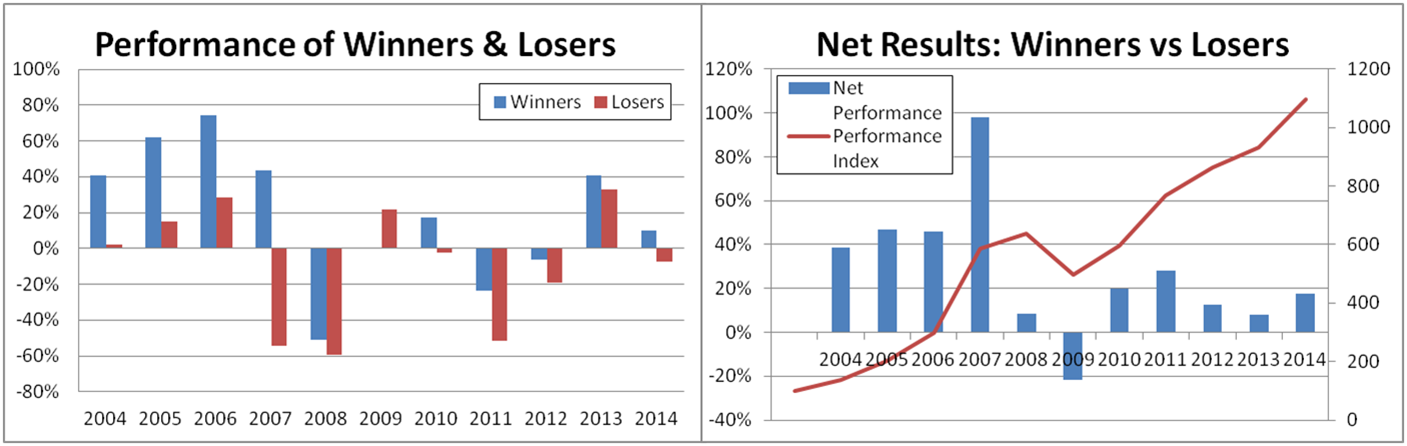
Data: Acadian Asset Management (Australia) Limited
The performance numbers above only focus on the active return piece and leave out cash returns, stock borrowing fees and transaction costs (in theory if you have long and short positions of the same dollar amount then you have 100% of the portfolio earning cash returns).
Digging deeper into the theory
This strategy is a simple one. In fact it catches two known theories in one strategy. First there is the cross-sectional momentum strategy between individual stocks, first identified in 1993 by academics Narasimhan Jegadeesh and Sheridan Titman (their paper was titled “Returns to buying winners and selling losers: implications for stock market efficiency”). However the strategy does not control for sector bets (nor did that of Jegadeesh and Titman) and so we are potentially exposed to a cross-sectional momentum strategy between industries. This has been shown to explain much of the performance of the individual stock effects described above. This was identified by Tobias Moskowitz and Mark Grinblatt in their paper titled “Do Industries Explain Momentum?”.
In practice …
In practice it is unlikely that we would see a strategy like this offered as an investment fund, since:
- The high volatility of the strategy may make it unpalatable
- The ability to borrow underperforming stocks may prove difficult and costly.
However in practice we find momentum is a strategy commonly applied by many fund managers, typically those who adopt a quantitative approach. Specifically most fund managers would control the size of the sector bets, hence ruling out the simple strategy presented here. Nonetheless many quant managers use momentum as an indicator of performance for stocks and sectors. It would commonly form part of a suite of signals; indeed I have never seen a fund manager offer a momentum-only stock strategy.
Takeouts
As stated last year: I am not recommending you replicate this ‘strategy’ – I wouldn’t myself. And as per last year I don’t tell you the current positions such a portfolio would be holding – you have to do your own homework! The point of this article is to remind you that there are many different ways to pick stocks. Some are based on company analysis, some are technical, and some are behavioural. You need to pick out an approach that you believe you can execute well, understand its strengths and weaknesses and the markets in which it will work well and in which it may struggle.
David Bell is Chief Investment Officer at Mine Wealth + Wellbeing (formerly Auscoal Super). He is also working towards a PhD at University of NSW. This article is for general education purposes only and does not consider the personal circumstances of any investor.