The world economy is experiencing massive shifts involving changes in consumer and business behavior. These shifts have largely been driven by technological advancements combined with where we are in the current business cycle. However, it may not be enough to own the companies behind this innovation and disruption, as these shifts are likely to create ongoing swings in profit pools over the next 10 years and beyond. It may be just as important to avoid companies adversely impacted.
It is critical to ‘know what you own’ in terms of profitability and earnings growth in such a complex market environment.
Earnings drive equity returns
Why do we spend so much of our time evaluating the potential earnings and profitability of companies? It’s because, over time, earnings generally drive equity returns, as shown below for 20 years between 1998 and 2018. Despite short-term dislocation, which is typically the result of substantive macro risks, stock prices usually reflect the earnings growth of companies. Show me a chart of a company’s earnings growth and I’ll show you a chart of a company’s stock price.
The strong correlation of earnings and equity returns
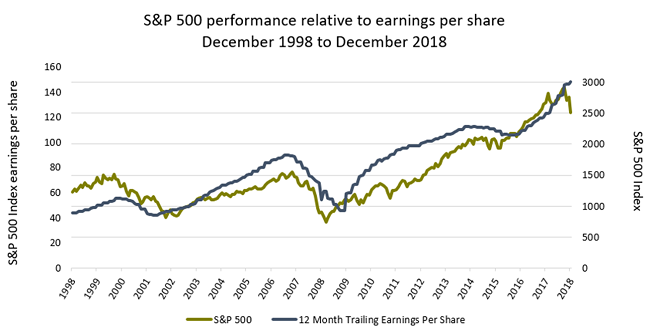
Source: Bloomberg, 31 December 2018
For example, US market earnings growth has been significantly higher than that of non-US markets in the wake of the global financial crisis, and thus we see the greater comparative advance of the US stock market.
The historical trend favouring quality
Another way to look at the dynamic between profitability and stock prices is through a quality lens that shows companies with positive earnings generally outperform companies with negative earnings by a significant margin, as shown below.
Quality has performed again after taking a breather
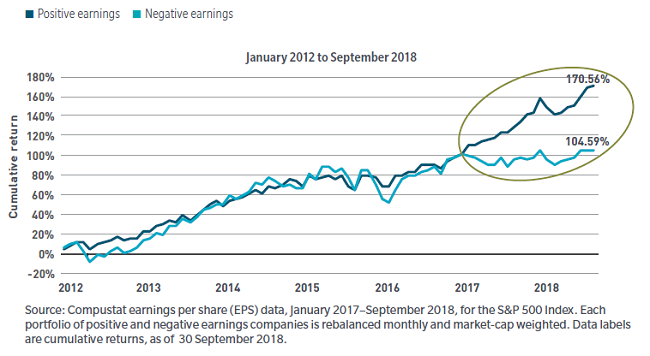
However, there are exceptions to this trend. From 2012 to the end of 2016, you couldn’t tell the difference between the stock prices of positive and negative earners. There were many reasons for this, including the global central banks accommodative policy creating massive amounts of liquidity, as well as the proliferation of passive investing. It was akin to an episode of Shark Tank in which the investors give money to entrepreneurs whether their ideas have merit or not. However, since 2016, the symbiotic dynamic of profitability and stock prices has been restored, which has led to the significant outperformance of the positive versus negative earners.
Differentiation and the alpha generation connection
We have witnessed this scenario play out in our own portfolios. From 2010 to 2015, company financial quality showed less differentiation, as the lower-quality companies we chose not to own generally outperformed. It’s no coincidence that this dynamic changed recently, when the Federal Reserve started raising interest rates in a consistent fashion, which also aligns with the charts above. We believe in overweighting companies that we value highly, as well as underweighting (or avoiding all together) stocks in the benchmark where we question the underlying fundamentals and future earnings potential.
In addition to higher rates, it’s becoming increasingly difficult for businesses to maintain a sustainable competitive advantage, or barrier to entry, to drive future earnings growth. This is largely due to the massive disintermediation in more traditional sectors and industries (an example is Amazon’s impact on bricks-and-mortar retailing) combined with peak profit margins for many companies at this stage in the cycle.
Nicholas Paul is an Institutional Portfolio Manager at MFS Investment Management. The comments, opinions and analysis are for general information purposes only and are not investment advice or a complete analysis of every material fact regarding any investment. Comments, opinions and analysis are rendered as of the date given and may change without notice due to market conditions and other factors. This article is issued in Australia by MFS International Australia Pty Ltd (ABN 68 607 579 537, AFSL 485343), a sponsor of Cuffelinks.
For more articles and papers from MFS Investment Management, please click here.