Last week’s US payroll number cemented the fact that over the last month or two ’good news is good news and bad news is good news’. Job losses in the US amounted to 20.5 million in April (and are still climbing) with the unemployment rate coming in at an eye watering 14.7%. Both numbers were the worst on record since the Great Depression.
The job losses will clearly weigh heavily on expectations for recovery, yet the equity market rallied nearly 2% on the day of release because these numbers were perceived as ‘good’.
Risk markets (equities and credit) are playing the old game we saw post the GFC. Bad news was greeted with glee by equity and credit markets given it meant more stimulus from central banks desperate to prop up inefficient economies and industries. Last week, the fact that bond futures started to price in negative interest rates got risk markets moving, despite Jerome Powell and the US Federal Reserve (Fed) explicitly saying they don’t like negative rates. In reality, negative pricing was a technical short stop and not driven by market expectations. However, many risk participants didn’t seem to care.
Did we learn from the GFC?
The lesson from the GFC was that despite the monumental volumes of stimulus from central banks globally, there were tremendous potholes along the way. Think European banking and sovereign crises of the last decade.
Today, the global economy has come to a complete stand still and yet some equity markets are now higher than they were pre COVID-19. Yes, there are some winners out of this but to have an entire stock market index trade above its starting point of the year is highly questionable.
The last decade was unique in that it was the first time in history that the US economy did not experience a recession in the entire 10 years. The US economy posted its longest expansion ever in over 170 years of data. In addition, the bond market yield curve inversion last year foresaw the current predicament with 3-month, 10-year and 2-year versus 10-year treasury rates inverting.
Of course, they didn’t predict COVID-19 but they didn’t need to. The economic cycle had gone on for way too long. This recession is not going to end after one month. It will take months and years of pain to work through this mess.
Liquidity will not solve the problem of bankrupt companies
The twitterised fast-paced 24-hour news cycle has sped everything up now, including expectations on how bad recessions can become. Recessions take a long time to play out (during the GFC in 2008-09 in the US it took 18 months) yet risk markets are arguing that it’s almost all over and things will be fine after only six weeks of pain.
Risk markets rallying 30% plus from the nadir of March is truly extraordinary and we believe way too much. Yes, we have seen the most aggressive response from central banks and governments in the history of mankind, which has spawned the ‘good news is good news and bad news is good news’ paradigm.
However, the Fed is reaching all the way into the fallen angel part of the junk bond market but liquidity will not solve the problems of bankrupt companies. It will only lower their borrowing costs and if you have no revenue or a fractured business model, it really won’t matter. It doesn’t replace revenue lost forever. And thus, we lurch from the liquidity crisis (which the Fed mostly solved) to the solvency crisis which will take years to play out. We believe equity markets over the past month have chosen to ignore this.
Unemployment spike in the US, delinquencies will follow
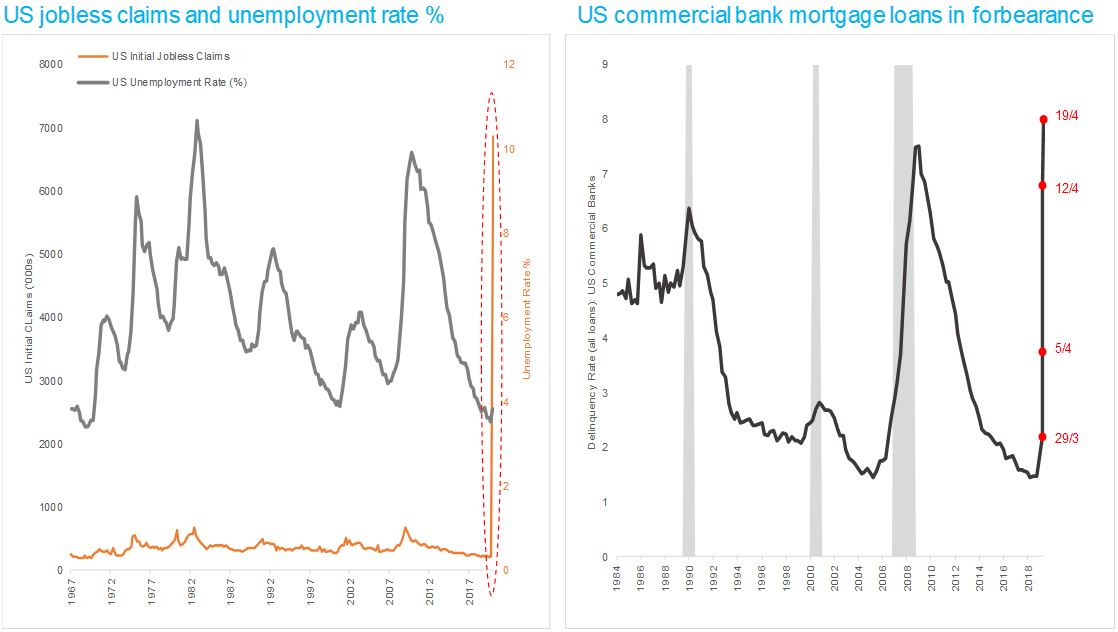
Source: Jamieson Coote Bonds, Bloomberg data.
We have a truly extraordinary amount of investment grade and junk bonds to refinance over the coming years with many of these industries hobbled into the future. We will see more pain emerge via the second- and third-round effects and it will hurt the investors and institutions they owe money to.
Refinancing risk - corporate debt maturities step up through 2021
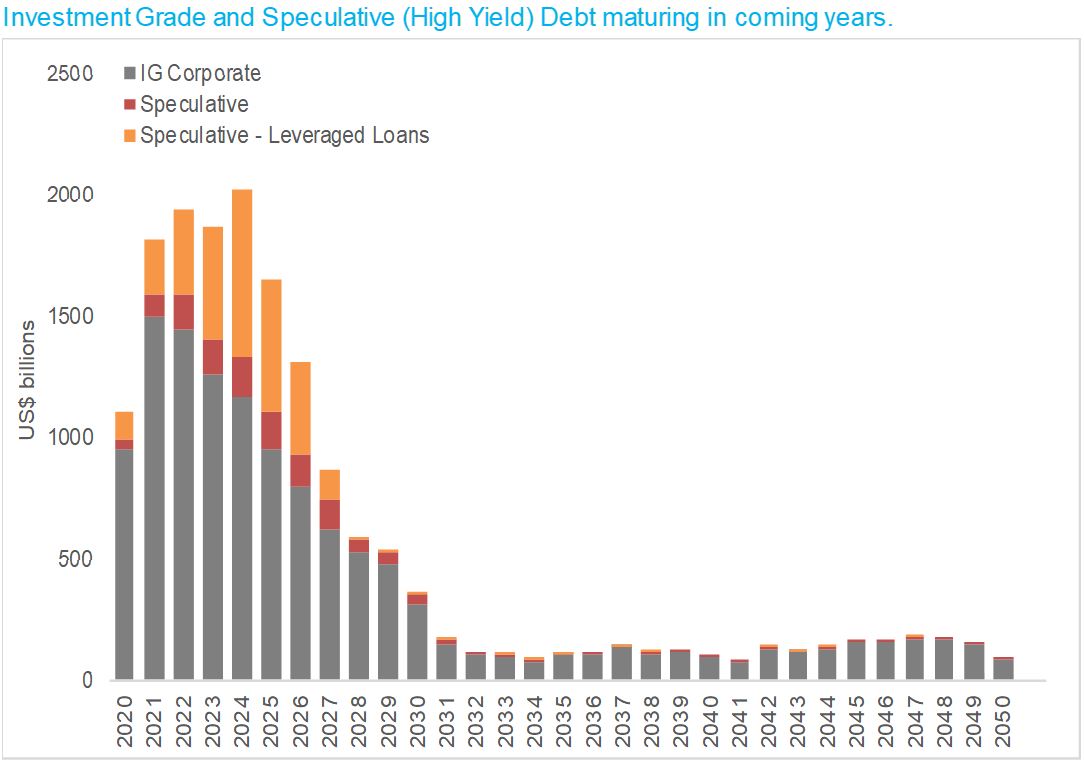
Source: Jamieson Coote Bonds, Bloomberg data.
Focus on a balanced portfolio
Risk investors shout 'Don’t fight the Fed' and they argue forward P/E ratios of 21 times on the S&P500 are cheap (this is the average P/E and the highest multiple since the Tech Wreck). This may be the case if you are a 25-year-old starting out in your career investing in growth stocks. However, we believe the optimists are misguided as they are betting on earnings growth or P/E expansion.
For a retiree or someone close to retirement who needs income, buying stocks with a P/E of 21 times can be incredibly dangerous. It will take the company 21 years of forward earnings for an investor to recoup the initial investment. For someone who retires at 65 with an average life expectancy at 85, investors might be well advised not to risk their wealth. Better to add balance to their investment portfolio by allocating a portion to more defensive assets.
Let’s not forget that the biggest buyer in equity markets over the past 10 years was corporations buying back their own stock. Printing trillions of dollars of debt to buy back equities was tax effective but as a consequence, a monster headache was created with so much corporate debt in the system. Now, an enormous structural buyer has been taken out of the market.
The limit of 'Don't fight the Fed'
We agree with not fighting the Fed, but only up to this point. We are now at an inflection where, barring a vaccine, good news is as good as it gets, and bad news is actually bad. We are truly at the hard part where we need to go back into work to pay down the massive amount of fiscal stimulus. We must open shuttered businesses and economies while avoiding the threat of Covid-19.
Employment will come back from the current 15-20% level but it certainly will not head back to the 3.5% pre-virus number in the US.
The question investors should ask themselves is how much pain will a 80% or 90% economy and all the multipliers of that 80% or 90% have on corporate profits and economies?
There are tremendous clouds on the horizon in the near and medium term, yet risk markets have separated themselves from the reality of economics. They have opened their finest bottle of champagne at 5am on the dawn of the recession.
Amongst it all, one thing we have seen over many cycles and crises is that the hangover will be brutal and the pain will last for years, despite whatever medicine Dr Fed prescribes going forward.
Angus Coote is Executive Director and Chief Operating Officer of Jamieson Coote Bonds (JCB). This article contains general information only and does not consider the circumstances of any investor.
JCB is an investment manager partner of Channel Capital, a sponsor of Firstlinks. For more articles and papers from Channel Capital and partners, click here.