A year ago, most people looking for a catalyst to stop the five-year surge in residential property prices probably focussed on unemployment or interest rates. In the background were Chinese buying and rising supply. As events unfolded, the impact of regulators and the Financial Services Royal Commission delivered the heaviest blows.
The extent of the price correction was described by Greg Paramor, former Managing Director of the listed property group, Folkestone (recently acquired by Charter Hall). He is a past president of the Property Council of Australia. In a private talk to clients last week, he summarised current apartment market conditions:
“When you get an over-exuberant market, it normally ends in tears, and we’re seeing some tears at the present time, particularly in the apartment market in Sydney, Melbourne and parts of Brisbane. Owner-occupiers in the right locations are still going well from people downsizing.
"But the people at the coal face who are doing the project marketing to investors say about two months ago, the market just stopped. They say if they dropped the price 20%, nothing would change. There are no buyers out there. We’ve seen this with the banking system going through its changes and the pull back from international demand, particularly mainland China. We are seeing a real problem develop in the investor end of apartments. The credit squeeze has stopped people in their tracks and anyone with money is sitting back and waiting.
"I think we’ll see some good buying opportunities in coming years, 2021 or 2022, we’ll be back where we started from where we haven’t got enough supply. But there will be an overhang of second-grade, investor-focussed, poorly-planned apartments.
"So the housing market is off, is it 10% or 15%? Will it be off 20%? Remember 1990. Possibly, it’s happened before, and it will happen again. That’s due to the recent over exuberance. We had a flat market from 2005 and it stabilised for a while, then it picked up strongly three or four years ago to above the long-term trend, and now it’s pulling back. Wage growth is nil and employment is full but these factors have become secondary to the availability of credit. If you have to sell, I’m sorry, you’ll have to weather a tough year or two, but the flip side for those wishing to enter the market, it’s a lot cheaper to get in now.”
Here is the latest data from CoreLogic, highlighted by the 7.4% fall in Sydney in the last year. Pockets of the apartment market are down much more.
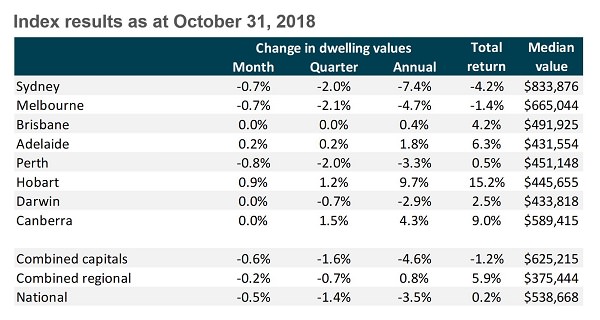
Source: CoreLogic
The price falls in a long-term context
The following chart from Stanford Brown’s Ashley Owen shows real (that is, adjusted for inflation) median house prices across Australia over almost 50 years. Most property owners have experienced good long-term returns, but there are often years of pain (I bought my current home in 1989 for $430,000 and three years later, after "the recession we had to have", it was worth less). Recessions usually result in price falls as unemployment reduces demand.
Sydney surged ahead after 2012, but the recent falls have wiped out a couple of years of gains. Melbourne also ran strongly. Perth is a standout for mediocre performance, still at GFC levels in real terms. Hobart has rallied recently, while Canberra is holding its gains. There is no one national market moving in a uniform way, and comparisons in the same city or suburb depend on the type of properties sold.
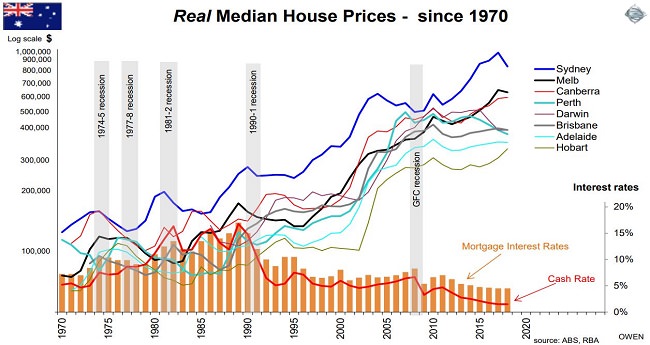
Click to enlarge
Owen’s chart shows rate movements and recessions, but he can’t show the changing lending policies in a chart. A couple of years ago, APRA became worried about too much investor interest-only lending, since the principal was not paid off, and introduced credit rationing. This was a mixed blessing for the banks, as it gave them permission to increase rates on their fixed rate mortgages. Then the Royal Commission found that banks and mortgage brokers had breached so-called responsible lending laws. These require banks to ensure borrowers accurately disclose their assets and liabilities, and the Commission revealed common practices of fudging the numbers by ignoring expenses and exaggerating income. Bankers have since become much stricter in who they lend to and what they require.
What is the outlook?
Macquarie Bank economists wrote a market note this week forecasting national dwelling prices will fall for at least another 12 months, with Sydney and Melbourne down 15% to 20% from their highs. These two cities contain 60% of Australia’s housing stock.
Most people who bought at the start of the surge have built up enough equity to accept this price fall as a typical correction. The most damage will hit those who bought a year or two ago with small deposits, and all their equity will be wiped out. There may be refinancing issues for those with three-year fixed rate deals, and property developers and builders are also vulnerable. The recent major bank financial results showed continuing low bad-debt experience, but the property market could fix that. At least Australia does not have the same system as in the United States where people with negative equity hand back the keys.
The loss of Chinese demand has been most dramatic in the investment apartment market. For years until 2016, Chinese developers delivered major projects to Chinese buyers who queued overnight to buy, and entire buildings sold out in hours. Most of this demand has disappeared along with the promise of capital gains.
Two further factors are on the horizon. First, a Labor Party win in 2019 may lead to implementation of their policies to tighten negative gearing eligibility and capital gains tax discounts. Second, the final report of the Royal Commission may force banks into even stricter lending conditions, especially if it results in fines for ignoring responsible lending laws.
A market that rises rapidly then gives back a quarter to a third of the gains is often seen as healthy, putting a lid on excessive exuberance. The correction appears orderly to date, but another 20% from here will leave far more on the table than a few tears.
Footnote: The acquisition of Folkestone by Charter Hall was completed this week. In seven years under Greg Paramor’s leadership, Folkestone grew from zero to $1.6 billion in funds under management. Following the acquisition, Charter Hall has $26.4 billion in property funds across office, retail, industrial and social infrastructure. Folkestone has been a strong supporter of Cuffelinks, and the sponsorship will now pass to Charter Hall. I have personally benefitted from many successful investments with Folkestone, and owe a thanks to Adrian Harrington for the close relationship which will continue at Charter Hall.
Graham Hand is Managing Editor of Cuffelinks. This article is for general information only and does not consider the circumstances of any investor.