Recent headlines on dividends have been primarily focused on the proposed removal of some of the more favourable tax treatments if the Labor Party secures government. While franking credits certainly enhance the attraction of dividends for many investors, we believe there are other reasons why the dividend income earned from an equity portfolio is an important element to consider when constructing an equity portfolio.
There are three key reasons why dividends have always been an important component for investors:
1. Dividends are a more reliable source of return than capital gains
Returns from equities come from two sources – capital appreciation and the dividends received from the shares held.
The returns from the S&P/ASX300 of these two components over the last 20 and 40 years are:
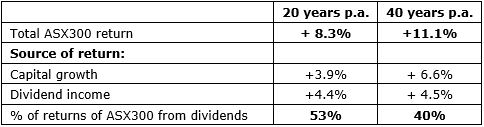
Source: Calculated using IRESS data indices
The importance of the dividend component of an Australian equity portfolio to investors is evident: around half of the returns of the S&P/ASX300 in the last 20 and 40 years have come from dividends.
2. The level of dividends received is not affected by the level of the sharemarket
While the level of capital returns from an equity portfolio over any defined period generally depends on the movement in the sharemarket, the level of dividends is dependent on the performance of the underlying companies, not the movement in share prices.
The level of dividends and the dividend payout ratio of any company is set by the Board of the company. It is generally a reflection of the overall profitability of a company and is independent on the level of its share price.
An investor’s level of dividends from a diversified portfolio – if made up of quality companies with the right attributes – should not vary greatly from year to year and is irrelevant to what is happening on the overall sharemarket, including during price falls.
Over the past 20 years, for the S&P/ASX300, the volatility of capital returns was 12.6% and dividend volatility was 1.0%.
Chart 1: volatility of returns of capital and income of the S&P/ASX 300 over 20 years
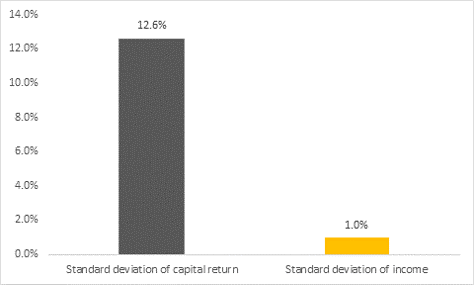
Source: IML, S&PASX300 31/03/1998 – 31/03/2018
Chart 1 shows that the volatility of capital returns has been high over the last 20 years, which is not surprising perhaps as it contains periods such as the tech boom and bust, the GFC, and the Eurozone crisis. However, the volatility of the dividends for an investor in the S&P/ASX300 has been very low.
This trend is true also on a year on year basis. Chart 2 shows the breakdown of the level of returns from the S&P/ASX300. The level of dividends paid (the orange bar) has been much less volatile than the level of capital returns (the blue bar) over the last 20 years.
Chart 2: Returns to shareholders over the past 20 years
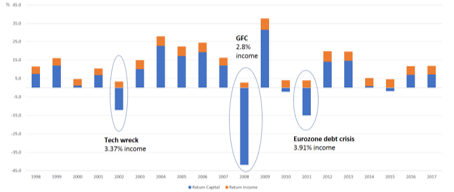
Click to enlarge. Source: IML and Morningstar Direct, S&P/ASX 300 01/01/1998 – 31/12/2017
Regardless of share price performance, the vast majority of companies in the S&P/ASX300 continue to pay dividends which to some extent compensates sharemarket investors for a share price often beholden to the whims of the market.
3. The dividend yield on stocks can act as a ‘safety net’
The movement in the sharemarket – particularly over shorter periods of 6 to 12 months - is often driven by market sentiment. This in itself is affected by predictions as to the future level of economic activity, inflation, and interest rates, as well as perceptions of geopolitical stability.
Often, minor events in hindsight from an economic standpoint can cause the mood of investors to sour markedly and lead to large declines in the sharemarket. For example, Iraq’s invasion of Kuwait in 1991 led to gloomy predictions about an impending global recession by many market analysts and economists.
A perceived crisis can cause many investors to panic, and the prices of shares can fall heavily initially, often indiscriminately and independent of their quality. Once the panic subsides, companies with sustainable earnings that can support a healthy dividend stream are often the shares that can recover the quickest.
The reason for this is fairly obvious. Rational long-term investors are always attracted to companies that pay a healthy dividend from a sustainable earnings stream. Once shares in quality companies fall to a level where the dividend yield is attractive, long-term investors buy these shares to ‘lock in’ attractive dividend yields, despite a volatile sharemarket.
Conclusion
Dividends provide sharemarket investors with a consistent part of their total return and can also act as a ‘safety net’ in down markets.
While the proposed changes to the tax-effective treatment of dividends in Australia via franking credits is potentially a negative development, dividends will remain an important factor when investing in the sharemarket. They will continue to provide investors with a relatively stable part of returns through the delivery of real cash flow, irrespective of the market cycle.
Fundamentals should remain crucial to deciding which companies ought to be included in a portfolio - mainly the quality and transparency of the earnings, cash flow generation, gearing levels, or balance sheet strength – which ultimately determines the level of dividends.
Anton Tagliaferro is Investment Director at Investors Mutual Limited. This information is general in nature and has been prepared without taking into account of the objectives, financial situation, or needs of any investor.