The simplicity of set-and-forget investment approaches is that once established, you don’t need to worry about them too much. Set … and … forget. It’s simple and it rhymes! You will still need to determine things like rebalancing and reinvestment policies but month-to-month, day-to-day, and minute-to-minute, there’s a reasonable chance of achieving your return objective over the long term by sticking to the plan. Indeed, obsessing over market gyrations can lead to investors making a mistake (for example, selling at the bottom).
Set and forget or remember to revisit?
This set and forget approach has been best exemplified in the strategic asset allocation (SAA) arena. Here, the realisation of long-term average returns and volatilities have combined with the benefits of diversification to help many to meet and exceed their objectives over several decades. Ten years on from the GFC, the central-bank-fuelled ‘bull market in everything’ rages on and proponents of SAA strategies can safely declare victory. Set and forget wins. Right?
Not so fast!
While traditional SAA strategies have delivered in the past, there’s no guarantee this will persist. In fact, we would argue that market conditions are such that an SAA approach will likely fail to deliver in the period ahead. Further, SAA has typically focused on the theoretical long term and realising long-term returns in a shorter-term reality may not happen. That reminds us of a famous quote whose true source is ‘unknown’ but is mostly attributed to part-time philosopher and full-time athlete, Yogi Berra, NY Yankee Baseball player:
“In theory, there’s no difference between theory and practice … in practice there is.”
Sometimes the long run is too long
Unless you have an infinite time horizon, you cannot necessarily rely on ‘long-run average market returns’ to deliver on your investment objectives. Historical averages don’t foretell the future. In particular, long-term averages don’t contemplate current valuations, future correlations, and certainly don’t consider the path to get there.
Taking each of those points in turn.
First, consider the elevated level of valuations across equities and fixed income (illustrated in the chart below), with P/E multiples at extreme levels and bond yields around record lows. The starting point matters, even for the theoretical long term. Even with a relatively optimistic outlook, it’s safe to say that expected returns in the period ahead are lower than seen historically.
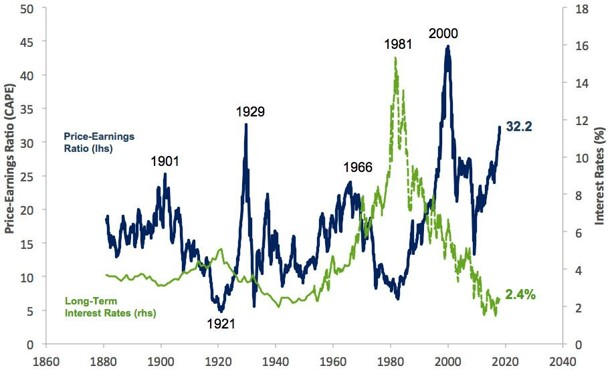
Source: Robert Shiller, Yale University, data to 31 December 2017. US 10-year sovereign interest rates or equivalent.
Second, the assumption that fixed income is defensive at all times and always offsets underperformance in growth assets is not borne out in the data. In fact, correlations between asset classes vary from period to period (see below). The average historical rolling 3-year correlation between global equities and global bonds of around 0.1 masks extreme changes in this relationship which has profound implications for diversification (maybe that lunch wasn’t ‘free’ after all).
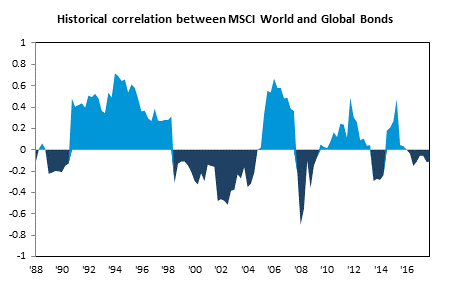
Source: Bloomberg, CFSGAM as of 31 December 2017. Rolling 3-year correlation based on quarterly data on the MSCI World Net Total Return USD and Citi World Government Bond Index (WGBI) USD Indices
Finally, and perhaps the most concerning of all, is that set and forget SAA strategies have never really contemplated the problem of sequencing risk (or the order in which events, often negative, happen). Those approaching retirement should care deeply about the path taken to achieve objectives, since there is much less time to overcome a major negative event such as a 40% equity drawdown. In this sense, SAA strategies have never really considered the retirement phase, and we believe investors with more defined investment horizons, should consider phasing out of SAA strategies at the appropriate time.
The options
So what options do investors have?
We believe there are three strategies:
- Do nothing: Accept potentially lower returns and/or higher volatility in an existing SAA strategy.
- Increase risk: Increase growth assets, ride the inevitable volatility, and hope for the best.
- Increase active management: This could take many guises, including more dynamic asset allocation strategies, allocations to alternatives or appointing more active security selection.
Despite the challenges outlined, we think achieving long-term objectives is possible without materially increasing portfolio risk.
Kej Somaia is a Senior Portfolio Manager at CFSGAM. This article is for general information only and does not take in account your individual financial circumstances.
For more articles and papers from CFSGAM, click here.