Kerry Francis Bullmore Packer would have loved superannuation and franking credits. In 1991, he was subpoenaed to appear before a Parliamentary Committee enquiring into the print media, and it was wonderful theatre. He bellowed out his responses and left most of the Committee members cowering. But his most memorable response came when asked about his company’s tax minimisation schemes:
"Of course I am minimising my tax. And if anybody in this country doesn't minimise their tax, they want their heads read, because as a government, I can tell you, you're not spending it that well that we should be donating extra!"
You may not feel quite as critical as Mr Packer, since our taxes pay for health, schools and pensions, but the superannuation system has been designed to encourage people to finance their own retirement, so it makes sense to use it. Income in superannuation is taxed at 15% in the accumulation phase, and personal marginal tax rates rise from 15% to 19% when earnings exceed $18,200, so income in superannuation is tax effective for anyone earning above this amount.
But that’s only half the story. Let’s put franking credits into the mix by understanding how dividend imputation works. Companies pay tax on their profits at a rate of 30% before dividends are paid to shareholders. In the hands of an investor receiving the dividend, the tax paid is called a franking credit or an imputation credit. For tax purposes, the shareholder receives both a cash dividend plus the imputation credit, and is treated as if they paid tax equal to the imputation credit.
The system operates like this to avoid double taxation of income. In effect, the shareholder receives back the tax that has already been paid by the company and instead pays tax at the investor’s own tax rate. If the owner of the shares is on a tax rate less than the 30% company tax rate, such as superannuation funds, they are entitled to a rebate of the overpaid amount.
Let’s consider a simple example. A company earns a profit of $10,000, and pays tax of $3,000, leaving $7,000. It pays this amount as a franked dividend to its only shareholder, which is a super fund. In its tax return, the super fund adds the tax already paid by the company to the cash dividend received. The 'grossed up dividend' is $10,000, and the super fund pays tax on this at 15%, or $1,500. However, it receives a credit worth $3,000 for the amount of tax already paid by the company, leaving a tax refund of $1,500. Neat!
So it’s a matter of relatively simple maths to calculate how much fully franked dividends is needed to offset the income tax due on the rest of a super fund’s portfolio, and therefore pay no tax, meaning that no investments need to be sold to fund the tax bill.
Skip the following box if you don’t have a mind for numbers.
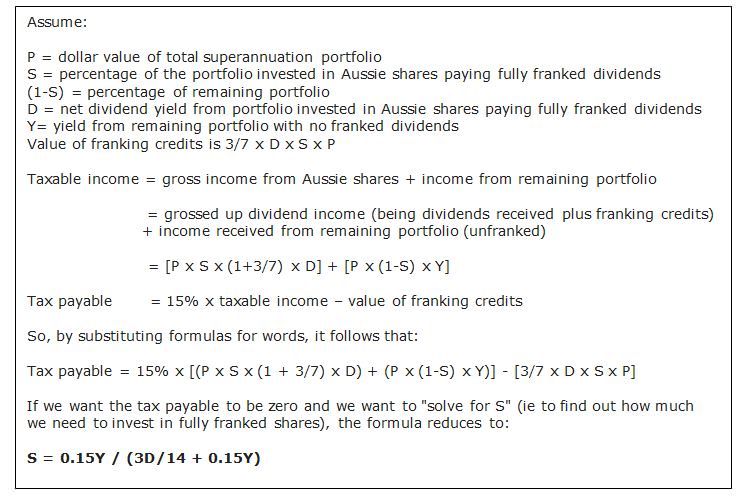
So with some current day numbers, this formula can be used with actual values for D (the dividend yield on the shares) and Y (the yield on the rest of the portfolio) to determine how much of a portfolio needs to be invested in fully franked shares to have a zero tax rate on the entire portfolio.
- a franked dividend yield on the Australian shares portfolio of 6%
- an unfranked yield on the remaining portfolio of 4% (eg term deposits).
The portfolio would only need to contain 32% of Australian shares paying fully franked dividends to have a zero tax rate. And without getting into a discussion on portfolio construction, most Australian super funds can justify an allocation to Australian shares of at least one-third.
The calculation ignores the impact of any realised capital gains and expenses from running the portfolio.
The combination of favourable tax rates and dividend imputation shows the power of saving in a superannuation vehicle. Once a fund converts to paying a pension, there is no tax payable by the fund on earnings. In this case, imputation credits are refunded in cash. Furthermore, if the pension recipient is aged over 60, then pension drawdowns are also tax free.
Kerry Packer would have loved it. All that income and no tax. And later, a refund from the government. Kerry probably learned a lot from his father, and maybe it's no coincidence that this powerful process carries the same name as that equally powerful man. Sir Frank.
