The year 2020 will be marked in history by a pandemic that had devastating effects on global health and economic activity. In financial markets, the pandemic set forth a rollercoaster of volatility that spotlighted the fundamental role of bonds in investment portfolios.
Making the case for bonds just 12 months ago would have been a difficult task. In June 2019, the share market was experiencing its eleventh straight year of growth following the GFC, and the ASX200 was a mere 500 points from its all-time record of 7,145. Equities were on an unbelievable bull run, and what would make anyone believe that it would not continue? Investor portfolios had not been tested in any serious fashion for more than a decade.
Lulled into a false sense of security
When markets feel at their best is perhaps when it is most paramount for investors to keep a perspective on their long-term goals. Whether those goals be for life in retirement, to ensure a well-being for others, or for philanthropy, an investment portfolio often entails a multi-decade horizon. It needs the ability to withstand the machinations of markets over various periods.
Going back to June 2019, many an investor considering a rebalance of their portfolio would have questioned the logic of diversifying away from outperforming growth assets—equities—and reallocating to bonds. High-quality bonds are boring—they are often synonymous with stability and income. It would have felt like leaving money on the table.
The vanilla nature of high-quality, investment-grade bonds, would have lulled many an investor into overlooking one of their most alluring qualities. Bonds are a diversifier in an investor’s portfolio, serving as ballast to equities in a market downturn. While there is a spectrum of bond offerings in the market, we are focusing this conversation on investment-grade bonds and the role they play in a diversified portfolio.
The market volatility during the first half of 2020 starkly displayed the differing characteristics between equities and other growth assets and bonds. This period provides valuable insights into how bonds can reduce all-in losses versus an all equity asset mix.
The chart below compares the daily return of a global bond and global equity portfolio between January and June 2020, scaled to 100 at the start of the year. The first thing that jumps out is the deep ‘V’ of equities in March relative to the muted dip in bonds. Both asset classes experienced a period of negative returns, but of significantly different magnitudes.
Equities have yet to fully recover. Equity optimists may point to the recovery of equities over a longer horizon, however, this article is not an argument against the long-term benefits of equity exposure, but rather how the two asset classes complement each other in a portfolio.
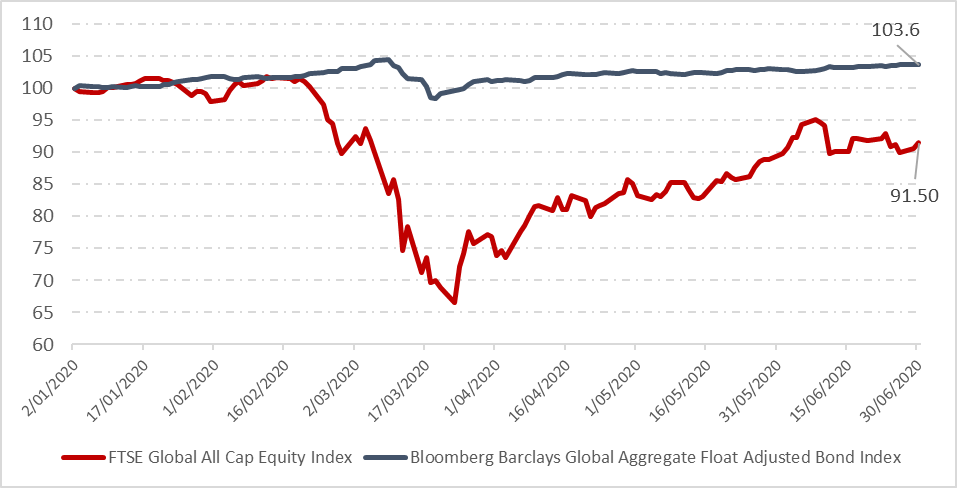
The wild, daily swings in March and April were enough to unnerve any investor, and the trap for investors was selling equities when things felt their worst—participating in the downswing, locking in losses, and missing the opportunity to partake in the recovery. Exposure to investment-grade bonds during this period served as a cushion, dampening overall portfolio volatility and potential losses, leaving an investor better placed to ride out the volatility and experience the equity rebound.
The diversifying impact of bonds
The table below compares global and local equity and investment-grade bond returns over the first half of the year. This period was exceptionally volatile, but it does a nice job at illustrating the diversifying effect of bonds. Over longer, less volatile periods, while the balancing benefit of bonds is more subtle, they still produce value for a long-term investor, especially if short-term market conditions trigger the need for realisation of losses in an overweight equity position.
While the prima facie return from bonds is modest across different phases of the first half of 2020, the differential with equities is large, as seen with the far-right columns. The comparative outperformance of bonds is in double digits for the half year, the first quarter and the month of March.
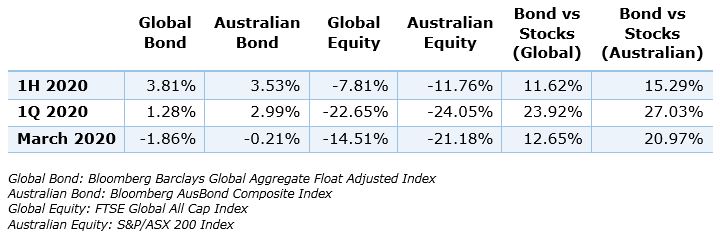
So here we are, in the second half of 2020, post one of the shortest and sharpest bear markets in history. Many investors who were overweight in higher risk asset classes would have coveted the downside protection that high-quality bonds would have provided. Even though equities have partially rebounded, most markets are sitting on losses year-to-date. Those with little diversification away from equities are probably feeling better now than in March, although the sting may not have fully worn off.
Check the role of different types of bonds
Recent history has shown there is no better time to appreciate and utilise the benefits of investment-grade bonds in your portfolio. There are different types of bonds available for investment, and each type and class play a role in a diversified portfolio depending on your investment goals, risk aversion, and time horizon.
High yield, lower quality bonds might fit in one person’s portfolio but not another’s. High-yield bonds do not provide the same degree of diversification from equity behaviour as investment-grade bonds. For this reason, investors must ensure they understand what their portfolio’s bond allocation is exposed to.
For those uncomfortable making the asset allocation between growth assets and bonds, there are diversified fund options to ensure you can still include a bond component in your portfolio, whether index investing, active investing or a mix of both.
As always, this should entail a consideration of your long-term goals, risk appetite and the fees you will be paying. That way, the lessons of 2020 will ensure bonds will be an important part of helping you achieve your investment goals, whatever they may be.
Geoff Parrish is Head of Vanguard's Asia-Pacific Fixed Income Group. Vanguard Australia is a sponsor of Firstlinks. This article is for general information only and does not consider the circumstances of any individual.
For more articles and papers from Vanguard Investments Australia, please click here.