It has been 10 years since the end of the 2003-2007 global China/credit boom, and it is time to check in on how stock markets have fared since then. The left chart ranks countries by their broad share price index growth over the past decade. Only 36 of the 62 main stock markets are ahead of their pre-GFC highs. The right chart shows average economic growth rates per country over the same period, in the same country order as the market performance, to demonstrate if economic growth relates to share price growth.
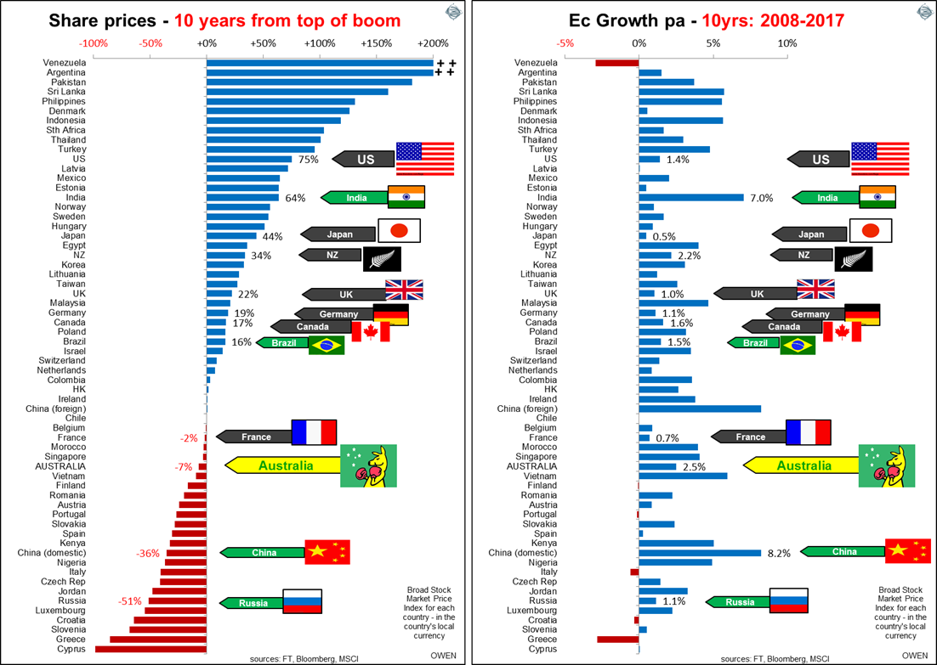
Among the ‘developed’ markets, Denmark won the gold medal in January 2013 for being the first stock market to surpass its pre-GFC peak, and it is now 126% ahead (i.e. more than double its pre-GFC peak). The silver medal went to the US in March 2013 and bronze went to the UK in May 2013. [See previous articles, Stock market Olympics, and the winners are and Australia can learn from gold medal winner, Denmark].
As usual there has been no statistical relationship between economic growth and share prices when measured across countries. Australia has been the so-called ‘miracle economy’ with the strongest long-term economic growth rate in the ‘developed’ world, and it did not even suffer an economic recession in the GFC, thanks to a deficit spending spree our grandchildren will be paying off. Yet the local stock market index (in price terms, not accumulation including dividends) is still behind its November 2007 high.
In contrast, the US, UK, Western Europe, Canada and even New Zealand suffered far lower economic growth rates in the GFC and over the past 10 years, but they have generated much stronger share prices than Australia. Denmark, the stand-out gold medallist stock market in the developed world, has had virtually no economic growth over the past 10 years. At the other end of the scale, China had the fastest economic growth rate over the past decade (and the largest aggregate growth in human history) but has had one of the worst stock markets.
Another common feature is that countries with the strongest stock markets often suffer political, economic or social turmoil and this was the case again - e.g. Argentina, Venezuela, Pakistan, Philippines, Turkey and Mexico.
There are many reasons for differences in share prices in different countries of course, but this quick snapshot is a useful reminder of the folly of focusing on economic growth as a pointer to share prices.
Ashley Owen is Chief Investment Officer at advisory firm Stanford Brown and The Lunar Group. He is also a Director of Third Link Investment Managers, a fund that supports Australian charities. This article is general information that does not consider the circumstances of any individual.