Based on current population growth in Australia, we are building too many houses. However, we are also still catching up on a long period of underbuilding, and with population growth picking up once again, the emerging construction downturn may be more gentle than feared. This article looks at the level of residential building activity against the demand from growth in households, and provides an overall assessment of the market.
The cyclical nature of housing
The housing sector tends to go through periods of overbuilding and underbuilding. We estimate that there was noticeable underbuilding from 2006 to 2013 which helped to fuel recent rapid house price growth. However, since 2014 we have been in a phase where we are building more homes than underlying need would suggest, as shown in the chart below. This growth in dwelling commencements has raised fears of oversupply, particularly in some capital city apartment markets. But overall, Australia’s housing market is still characterised by relatively low vacancy rates and positive rental growth.
With an upturn in national population growth and an easing in forward indicators of housing construction based on residential building approvals, the gap between building activity and underlying demand looks set to close.
Dwelling supply and demand in Australia
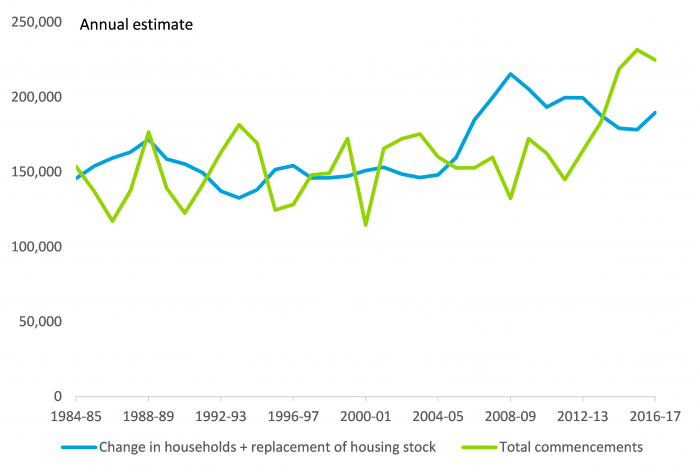
Source: Australian Bureau of Statistics, Deloitte Access Economics
Building activity moderating as growth driver
Residential building approvals peaked in the second half of 2016 and have retreated modestly since. This has been driven largely by a fall in apartment approvals, particularly in the high-rise segment. The fall in residential building approvals likely reflects factors such as tighter developer financing, higher taxes on foreign investors (levied at the state level), fears of oversupply and limited future price growth. This indicates residential building activity, which has been a driver of economic growth, is set to moderate.
Against this moderating supply outlook, population growth has surprised on the upside. Spurred by an increase in net overseas migration, national population growth was over 389,000 over the year ending March 2017 (up from over 343,000 the year to March 2016). This has tempered expectations of an oversupply of housing, although dwelling completions will remain elevated in the short term.
The supply-demand balance has been an important driver of recent strong house price growth, along with low mortgage rates and strong investor interest. CoreLogic’s Home Value Index shows price performance varies significantly across the country. Long-time standouts Sydney (+10.5%) and Melbourne (+12.1%) have continued to record robust growth over the year ending September 2017. The relatively affordable Hobart (+14.3%) has seen substantial price growth amid a healthier local economy while the Canberra market (+7.8%) has also been a solid performer. Other markets have been more mixed, with Perth (-2.9%) and Darwin (-4.7%) still experiencing falling prices amid challenging local economic conditions.
More recently however, national price growth looks to have slowed, with CoreLogic’s five capital city aggregate up by a more sedate 0.6% over the past quarter, or around 2.5% price growth on an annualised basis. This may reflect a range of factors domestically, such as stretched affordability (particularly in Sydney and Melbourne) in a low wage growth environment, tighter lending standards (and a crackdown on interest-only loans) and increases in mortgage rates by major lenders. It may also reflect an easing in foreign investment, with higher foreign investor taxes (for example, New South Wales’ stamp duty surcharge for foreign investors recently increased from 4 to 8%) and a continued clamp down from Chinese authorities on capital flight.
Good prospects for balanced supply and demand
As a result, while there are still many risks in Australia’s housing market (and far too much household debt for comfort), the short-term outlook might be more about balance than wild swings – and prices levelling out at a time when housing activity moderates and population growth remains buoyant.
David Rumbens is a Partner and Andrew Ponsonby is a Senior Analyst at Deloitte Access Economics. This article is reproduced with permission.