By now most investors are tiring of their email in boxes filling with economists and strategists talking about reflation (that is, a recovery in spending and economic growth), how much more optimistic they are relative to consensus, and for how much longer the reflation trade will persist.
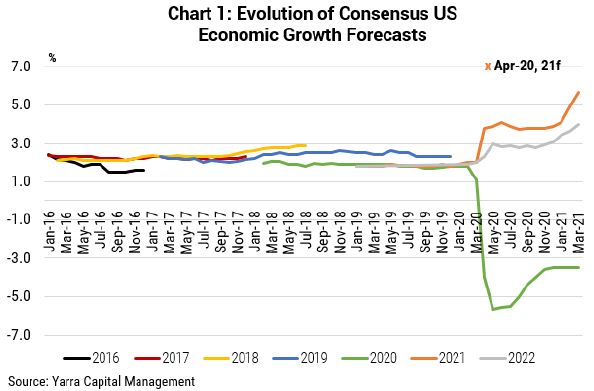
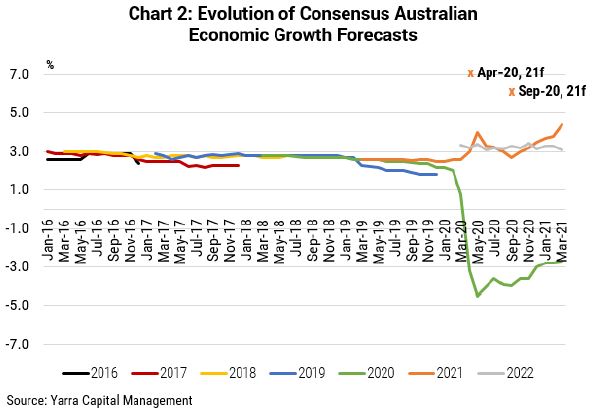
There were very few people talking about a strong V-shaped recovery this time last year. Indeed, a scan of the forecasts of leading sell-side economists in April 2020 shows consensus forecasts of 3% for the CY21 for Australia and 3.8% for the USA.
A switch to stronger growth forecasts
Indeed, peak pessimism was not reached until September 2020, when economic growth downgrades ceased and modest upgrades commenced. Currently, consensus for CY21 has risen to 5.7% in the USA and 4.4% for Australia.
In contrast, our forecasts for the US in 2021 – which we published in mid-April 2020 – was 6.5% (represented by the cross in Chart 1). For Australia (Chart 2) we were even more optimistic, forecasting 7.0% economic growth. As we moved through 2020, it was clear the expected contraction in economic growth in 2020 was less than expected and we reduced our forecast rebound in Australia’s economic growth in 2021 to a still sizeable 6.0%.
Much of our more upbeat analysis was based on:
- the nature of the shock being more akin to a natural disaster
- the quantum of the fiscal packages
- excess credit growth
- the outlook for vaccine development
- the prospect of pent up demand.
One year on, the clambering to upgrade growth estimates has only intensified. Over the past two months, consensus forecasts for Australian economic growth in 2021 have been upgraded a further 0.7%. In the USA the revision over the past two months is a remarkable 1.6%.
For Australia. we remain 1.5% above the consensus forecast and around 1% above the most optimistic other forecaster. What supports our optimism?
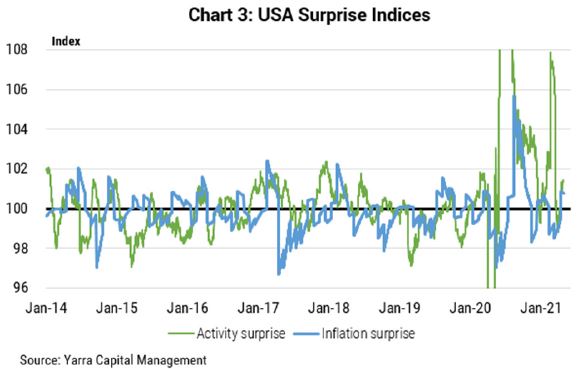
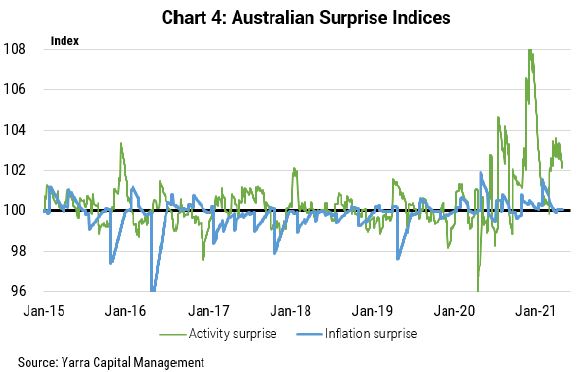
1. Australia’s data consistently beats economic forecasters
Charts 3 and 4 show our calculation of economic data surprises for economic activity and inflation relative to consensus forecasts (US vs Australia). A positive reading represents economic data beating consensus expectations weighted by data importance and time decay.
Clearly, Australia’s economic activity data is not only continuing to beat increasingly upbeat economic forecasts, the positive data surprises are larger in Australia.
2. Real economic growth is expanding at pace
Our 'nowcasting' techniques (Chart 5) for gauging in real-time how fast the economy is expanding already suggest that real economic growth was expanding at 4% yoy by the end of 1Q2021.
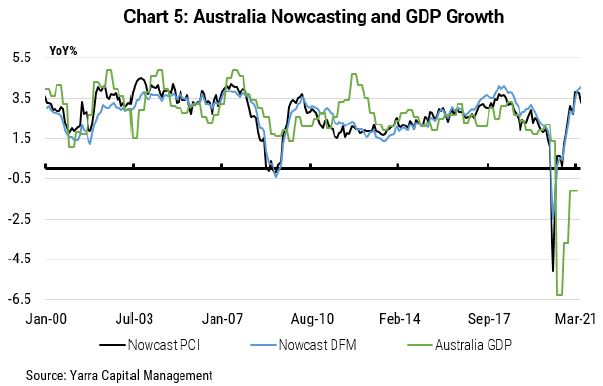
Note: Our nowcasting methodology is to estimate real time economic growth via both dynamic factor models and principal component models for each of the major economies to provide an alternative underlying picture of economic growth to the often noisier official GDP data.
3. Treasury’s projections have been comfortably exceeded
Much stronger economic growth, much lower unemployment and much stronger commodity prices have combined to already deliver a $23 billion better fiscal outcome relative to Treasury’s December projections and closer to a $50 billion saving over the next four years.
The question for Q2 is how much more of an 'economic surprise' dividend will likely flow through the Budget and what will the Government do with it?
We believe the Treasury’s growth figures are 0.5% too low for 2020-21 and 1.25% too low for 2021-22. The unemployment rate is likely too high by as much as 2%. And an iron ore assumption of $55/tonne embedded in the Budget is one-third of the current iron ore price. Clearly there are further major revenue upgrades to come.
Our take is that the May Budget will be used mainly to evidence the vastly better Budget and economic outcomes that have been achieved. We expect the true election Budget will come in late 2021 (i.e. mid-year Budget), with more strategic spending and tax changes announced to setup a May 2022 Election. The combination of the Coalition’s political challenges and the Budget’s economic windfalls will likely spark additional fiscal spending later in 2021, sufficient to bolster economic growth expectations.
Momentum to continue over 2021
Mid-2021 will likely mark the peak of global economic data surprises and the final phase of economic growth upgrades. Nevertheless, we believe there is more oxygen in Australia’s economic recovery and that consensus has long been too slow to recognise the domestic economy’s capacity to expand at close to 6% through 2021.
While this will set off expectations of a higher cash rate ahead of the RBA’s 2024 guidance, the RBA can be expected to attempt to allay those fears by making the case that inflation expectations and wage growth remains too low to be consistent with their inflation objective. Nevertheless, the likely RBA growth upgrades will almost certainly end the prospect of the RBA rolling the 3-year bond beyond the April 2024 target. Together with the end of the Term Funding Facility in mid-2021 the reality is that a very modest tightening cycle is already commencing.
Tim Toohey is Head of Macro and Strategy at Yarra Capital Management. To the extent that this article discusses general market activity, industry or sector trends, or other broad based economic or political conditions, it should be construed as general advice only. References to ‘consensus’ throughout relate to Bloomberg consensus unless otherwise stated.