Hurricanes Harvey, Irma and Maria may have smashed parts of the US in 2017 but Janet Yellen’s Federal Reserve was determined to persist with an unprecedented way to tighten monetary policy. By October, the central bank commenced selling assets on its balance sheet to unwind eight years of on-and-off quantitative easing.
Investors wondered: What would happen when the Fed shrank a balance sheet that had swollen from US$900 billion in 2008 to US$4.4 trillion by 2017 (by not reinvesting as much as US$50 billion in bonds that matured every month)? Some turbulence eventuated, but things went smoothly enough for a Fed led by Jerome Powell from February 2018 (until they didn’t).
By September 2019, the Fed balance sheet had shrunk by about US$600 billion. Strains in the repo market spilled into the money market and the secured overnight financing rate jumped from 2.43% to above 5%, an event the Fed described as “surprising”. To ensure short-term interest rates behaved, the Fed restarted asset purchases.
The Fed’s expanding balance sheet
Assets: Total assets (less eliminates from consolidation): Wednesday Level (WALCL)
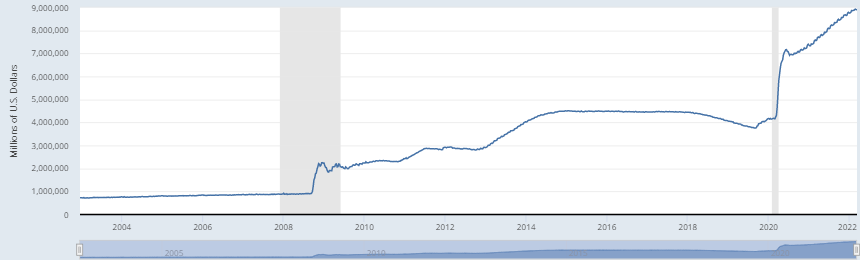
Source: Federal Reserve of St Louis. FRED economic data. Shaded areas signify recessions.
Investors might keep this episode in mind when the Fed restarts asset sales accompanied by at least the Bank of England.
To understand what might happen when the biggest buyers of debt become the biggest sellers, it helps to revisit what happens when central banks undertake quantitative easing. Under the non-conventional policy, a central bank creates money (electronically) as an asset on its balance sheet and buys financial securities in the secondary market with interest-paying reserves. The purpose is to reduce long-term interest rates. Quantitative tightening, as the name suggests, is the reverse process. Once central banks ‘destroy’ money, long-term interest rates should be higher than otherwise.
Why do central banks need to reduce their balance sheets? A valid answer is they have no need to. The bloated balance sheets are not causing financial instability, even if pumping them up comes with side effects such as asset inflation and excessive risk-taking and is a culprit behind consumer inflation.
But central banks are intent on shrinking their balance sheets. The main reason is central bankers worry that an overstuffed balance sheet could shake the financial system. At some level, the public might lose confidence in the value of their fiat money. Central banks fret that the extra reserves they create might be lent out and inflation might accelerate. They worry too the policy option is, in Powell’s words, “habit-forming”. By this, Powell meant it’s another ‘Fed put’. This is slang for the moral hazard whereby investors take more risk because they are confident the Fed, to protect the economy, will act to cut their losses.
Another reason for quantitative tightening is political. Quantitative easing has led some to accuse central banks of making it easier and cheaper for governments to run fiscal deficits. Reversing the process would depower those accusations.
One motivation the Bank of England has for selling assets appears to be that higher short-term interest rates could turn central bank profits into losses for government budgets. If short-term rates rise enough, the interest central banks pay on their balance sheet liabilities will exceed the interest they earn on their assets. The bigger the balance sheet, the bigger the losses. The Fed would be aware of the political storm created if it were to become a loss-maker for Washington.
It’s notable that the Fed and the Bank of England talk of undertaking quantitative tightening in a “predictable manner”. That’s probably because so much surrounding the stance is unknown. No central bank has ever reversed its asset-buying over the medium to long term.
The danger today is that central banks want to shrivel their balance sheets when they are raising their key rates to combat inflation at decade highs. No one knows how high bond yields might rise as central banks raise their key rates and shrink balance sheets, especially if inflation accelerates further. Nor does anyone know how high bond yields could rise without triggering the financial mayhem that occurs when investors anticipate a recession.
But the bigger menace of quantitative tightening is that it might show the Fed is not serious about curbing inflation. Even though all US inflation gauges have exceeded the Fed’s comfort levels for months, the Fed is buying assets until the end of March. A Fed that couldn’t immediately end asset purchases when inflation first reached 5% mid-last year is unlikely to allow asset sales to destabilise markets. It’s likely that if trouble comes, the Fed will cease asset sales or even resume asset buying. With the cash rate close to zero, quantitative easing is the best Fed put around. Don’t be surprised if it resumes.
To be sure, the pressure is mounting on the Fed to control inflation. But adjusting the key rate will be the means to curb price rises, not asset sales. A Fed balance sheet at double the size of 2018-2019 must be riskier to puncture without mishap – so even timid asset selling could stir trouble. The risks will increase if other major central banks join in. An inflation outbreak that requires an abrupt tightening of monetary policy could escalate the risks of doing nothing about a swollen balance sheet.
Amid the uncertainty, it’s best to frame the Fed’s balance sheet as a tool to ensure today’s asset bubbles don’t burst. The longer-term problem, of course, is that one day the Fed put will be kaput. Investors might confront a hurricane.
Michael Collins is an Investment Specialist at Magellan Asset Management, a sponsor of Firstlinks. This article is for general information purposes only, not investment advice. For the full version of this article and to view sources, go to: https://www.magellangroup.com.au/insights/.
For more articles and papers from Magellan, please click here.