‘Peak oil’ is a phrase that has been around for some time, but some industry watchers believe that we may have now already reached that milestone.
While the world is currently in the grip of the COVID-19 pandemic and its effects are grabbing the headlines, in a decade’s time - from a purely economic perspective - COVID-19 may be seen just as importantly as ringing the bell on oil, which has been the dominant energy source for the past century.
Demand for oil may never reach prior levels
BP PLC, one of the seven global ‘supermajor’ oil companies, has called the top for oil, saying that demand will never again reach pre-pandemic levels and will be, in its most bullish case, broadly flat for the next two decades. Fossil fuel demand will be challenged by other power types, namely electricity, which will be supplied by a growing grid of cheaper solar and wind sources.
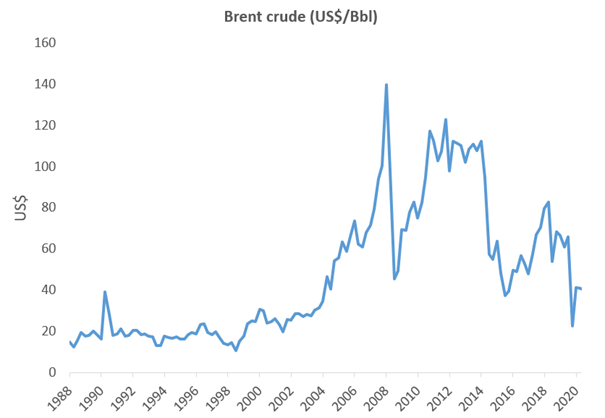
Source: Bloomberg
Others believe global oil demand could rise above pre-COVID levels by mid to late 2020s before declining. Oil demand may rise from 91.7 million barrels a day (MMbls/d) this year to slightly above 100MMbls/d by the mid-2020s. In a conservative net zero emissions (EU + China) case, brokers are predicting oil demand will then fall to 75MMbls/d (a decline of ~25% from 2019 levels).
Where the OECD and China pursue net zero carbon outputs, oil demand could fall to 54MMbls/d (-45%) by 2060. In a net zero (all countries) scenario, demand could fall to as low as 21MMbls/d (~-80% from current levels).
For its part, French oil giant Total SE (another supermajor) has set out two likely future scenarios:
In its first scenario, which it has called 'Momentum 2050', there is a green deal in Europe, while outside of Europe actions are based on individual country carbon targets. There is also aggressive deployment of proven technologies such as EVs, solar and wind, and biofuels. Under this scenario, 60% of cars are electric and sustainable aviation fuels make up 15% of total demand by 2050.
In its second, more extreme scenario, called 'Rupture 2050', all countries commit towards net zero carbon emissions with strong shifts in public policies as well as technology breakthroughs in new industries like hydrogen, synthetic fuels and carbon capture. Under this scenario, it has 75% of cars as being EVs and 60% of aviation being sustainable by 2050.
For Total, it is not that energy demand will dwindle – all of its scenarios see an increase in demand for energy globally – but that low-carbon power will increase its supply.
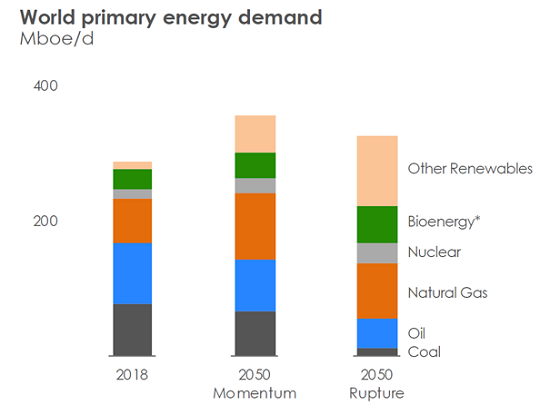
Source: Total
Under both scenarios Total is anticipating oil to peak in the coming decade, saying demand growth will end around 2030 and then decline due to the electrification of end uses, transport transformation and the greening of the petrochemical industry.
What about the supply side?
As we all know however, the oil price is a function not just of demand but also of supply. Will we see another cycle in the oil price in the next decade as supply falls to match demand, or is the fall in demand sure to make it all downhill from here?
The first point to make is that not everyone agrees that peak oil is here or is imminent. Oil remains the standard from which all other power sources are judged and is seen by many in the industry (and OPEC) as the only commodity that can satisfy the demands of an increasing global population and expanding middle class.
However, even a long-term price of US$40 a barrel does not necessarily mean value destruction for the lowest-cost oil majors in the medium term. Rather, the lack of incentive to invest in new fields could see them run down their reserves and not drill new wells, increasing free cash flow in their fossil fuel operations while they pivot towards delivering power from carbon-free (renewable) sources.
The other alternative could be that the fall in investment because of low oil prices and the subsequent supply shortfall in the medium term triggers another oil price hike in the 2020s, before we see another top out of prices in the 2030s as electricity makes more of an impact, i.e. we will see one last oil price cycle.
Contrarian investment opportunities
For the moment, investors in oil-related equities are relying on price levels remaining at current levels, i.e. that we will not see another cycle of oil prices rising on the back of a supply-side squeeze. This may present an opportunity for the judicious (and somewhat contrarian) investor.
We are understandably cautious about the oil industry but given the cheap valuations in the sector it would be unwise to ignore it. For our part we hold Royal Dutch Shell in the global portfolios. We believe Shell is well placed to perform in the coming years, having adapted its cost structure to operate in the current low-price environment. Shell is capable of paying a 5% dividend yield even if the oil price stays low.
In the past few years, Shell has also transformed its upstream portfolio, having divested its high cost projects and invested in offshore projects which will yield significant returns as oil demand continues to recover from its pandemic lows.
Relative to other oil majors, Shell is better placed as the energy complex transitions away from oil, being the industry leader in gas (LNG) and will benefit as governments worldwide reduce their reliance on energy generation from coal. Furthermore, Shell can leverage its substantial retail network and differentiated trading capability to creatively profit from the shift to renewable and green energy.
Douglas Huey is a Portfolio Manager at PM Capital. The content reflects opinions as at the time of writing and may change. PM Capital may now or in the future, deal in any security mentioned. It is not investment advice.
[1] Source: Bernstein