It’s why millions of dollars are spent on Grand Prix qualifying cars and house prices are higher near good schools. The better your starting point, the more likely you are to succeed.
Long-term investing is no different. The lower the starting price of an investment, the better it is likely to do, all else being equal. At its heart, a company’s stock price is made up of not just of what its assets, ideas and people are currently worth, but also the profits the market expects it to generate in the future.
Is the value already in the price?
The higher the valuation, the more of those future earnings are already included in the price and the better the company has to do just to meet those inflated expectations, let alone surpass them. In addition, the higher investors’ expectations, the greater the number of possible scenarios wherein the company disappoints the market. Conversely, the lower the starting price, the less the company has to do to beat low expectations.
When it comes to long-term investment returns, your starting point matters
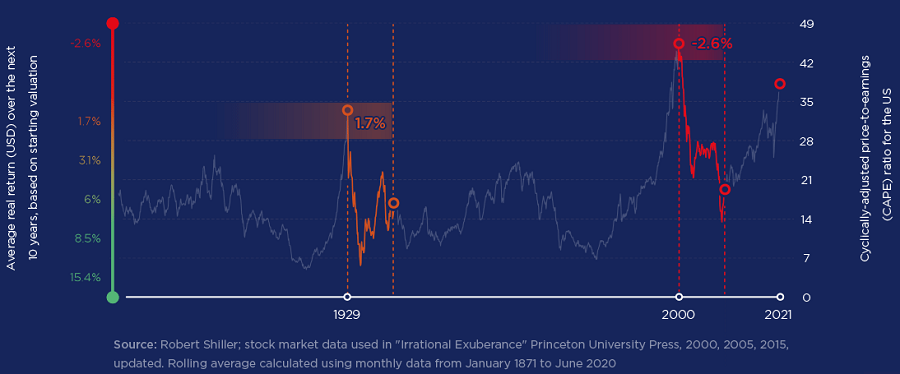
The chart above demonstrates this. It plots the average cyclically adjusted price-to-earnings (CAPE) ratio for the US market over the past 140 years. The CAPE ratio is calculated in a similar way to the standard price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio, but instead of dividing a company’s stock price by one year’s worth of earnings, it uses the average earnings figure for the past 10 years (adjusted for inflation) to smooth out the impact of economic cycles.
Investors tend to use the CAPE ratio as a barometer for how expensive or cheap a market is. A high CAPE ratio tends to indicate that the market is expensive, with the long-term average for the US market somewhere around 17 times.
As you can see, US stockmarkets in aggregate have seldom traded above 30 times. In other words, there have been few times in the past 140 years when investors were willing to pay for more than 30 years’ worth of average earnings upfront and, when they have, the average real return over the following 10 years has been underwhelming, to say the least.
Markets looking expensive in aggregate is not just a US phenomenon. A similar case can be made for the broader FTSE World Index, albeit over a shorter time frame. Over the past 30 years, when the median stock in the FTSE World Index has traded at a starting P/E ratio above 30 times, investors have never made a positive real return over the following four years. At the end of October 2021, the median stock in the FTSE World Index traded close to 30 times.
What does that mean for investors today?
Judging from the chart above, the prospect of stellar returns at an aggregate level over the next few years looks modest at best. If one looks below the headline level, at the individual stocks that make up the market, however, much of the increase in recent years has been driven by a handful of expensive stocks that have become extremely expensive, rather than a groundswell of growth that has pushed up the whole market.
Among those companies that have been left behind, there is a great deal of opportunity to be found, even in a market that is as expensive as the US.
One such example is AES, an independent power producer listed in the US, and a stock held by the Orbis Global Equity Fund. A popular theme for many investors at the moment is the energy transition space, and companies positioned to benefit have been rapidly and, in some cases, extremely bid up. As such, it’s been hard for many investors to find good value in this area. In our view, AES is a rare exception, given it currently trades at around 15 times forward earnings, significantly lower than its peers such as NextEra Energy, which, despite similar levels of earnings growth, trades at more than 30 times forward earnings.
Part of the reason this discount exists is AES’s history and, in particular, its rapid, early expansion. Founded in 1981 as an energy consulting firm, it soon moved into energy generation. By 1988 it had become the largest independent power producer in the US and by 2002 was operating in 29 countries. But, while its share price rose dramatically during these years, it also took on considerable foreign exchange risk, overpaid for assets and consistently missed estimates.
Since 2012, however, the firm has been under new management and overseen a fairly dramatic transformation. While, at a headline level, the firm still does most of the same things, where and how they do them has been significantly improved. Not only has its foreign exchange exposure been dramatically reduced by both its shrunken global footprint and the fact that now around 85% of revenues are denominated in US dollars, but more importantly it has become a leader in green power.
At first glance, AES might not appear very ‘green’ given currently around 25% of the company’s total electricity production is from coal. But, the remainder is derived from renewables and natural gas, and AES is aggressively moving away from coal. Indeed, AES expects coal to account for less than 10% of its total electricity generation in 2025. In addition to its core unit, AES also owns an energy storage joint venture with Siemens called Fluence, currently the second largest energy storage provider globally – second only to Tesla. Management expects Fluence revenue to grow from $100m in 2019 to around $3bn by 2025, with the potential of real blue-sky upside. More recently, Fluence was listed separately, making it one of the largest pure-play energy storage companies in the world. On top of that, late last year, AES announced a 10-year strategic partnership with Google, which we believe, should help to expand its renewable energy project pipeline.
There are, of course, risks to the thesis. AES does have a history of overpromising and underdelivering, albeit under previous management. Then there is the fact that increased competition within the renewables space would put downward pressure on the economics of selling power. And, there does remain some forex risk, especially as not all of its assets are in politically stable jurisdictions. However, we believe these risks have been priced in.
The market overlooks some sectors
And, AES is not alone. There are many other examples, all over the globe from technology to healthcare, from banks to logistics, of companies that are being overlooked by a market focused on a small subset of existing winners.
As bottom-up stock pickers, we are able to search underneath the uncomfortable heights of the headline indices to find exciting opportunities at compelling valuations. By focusing on the starting point and the price we pay, we think this increases the likelihood that we will be successful over the long-term.
Shane Woldendorp, Investment Specialist, Orbis Investments, a sponsor of Firstlinks. This report contains general information only and not personal financial or investment advice. It does not take into account the specific investment objectives, financial situation or individual needs of any particular person.
For more articles and papers from Orbis, please click here.