The ‘economics of retirement outcomes’ is a concept that explores how economic developments can affect retirement outcomes. Not everything in retirement is subject to market returns or the decisions of individuals, financial planners or super funds. The current soft labour market is a case in point.
Soft labour markets: unemployment increasing and negative wage growth
Currently labour market conditions in Australia are soft. It is one of the more significant challenges faced by the Australian economy. Our unemployment rate recently touched 6.4% (the highest level in 12 years) before dropping back marginally to 6.3%. Just 18 months ago the unemployment rate was 4.9%.
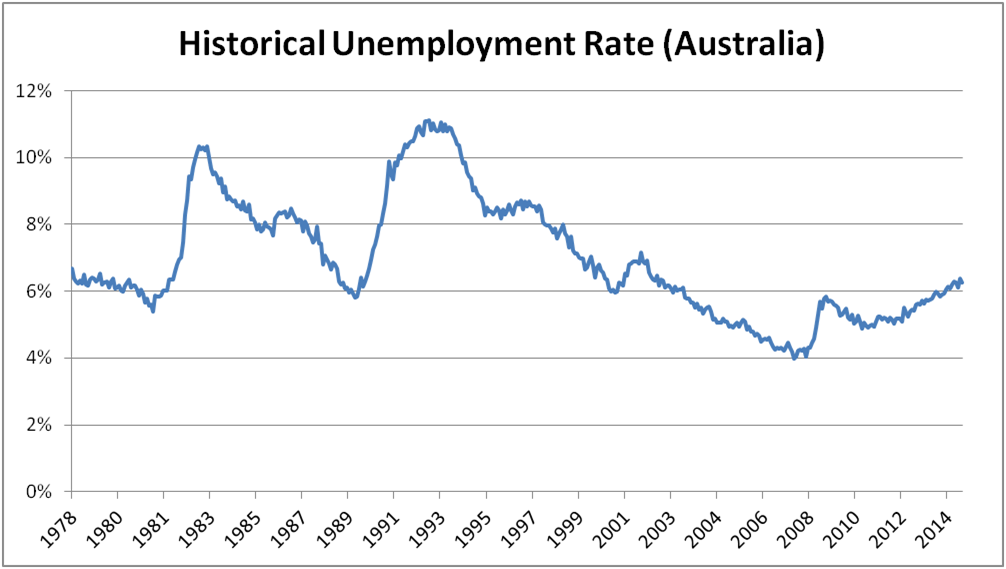
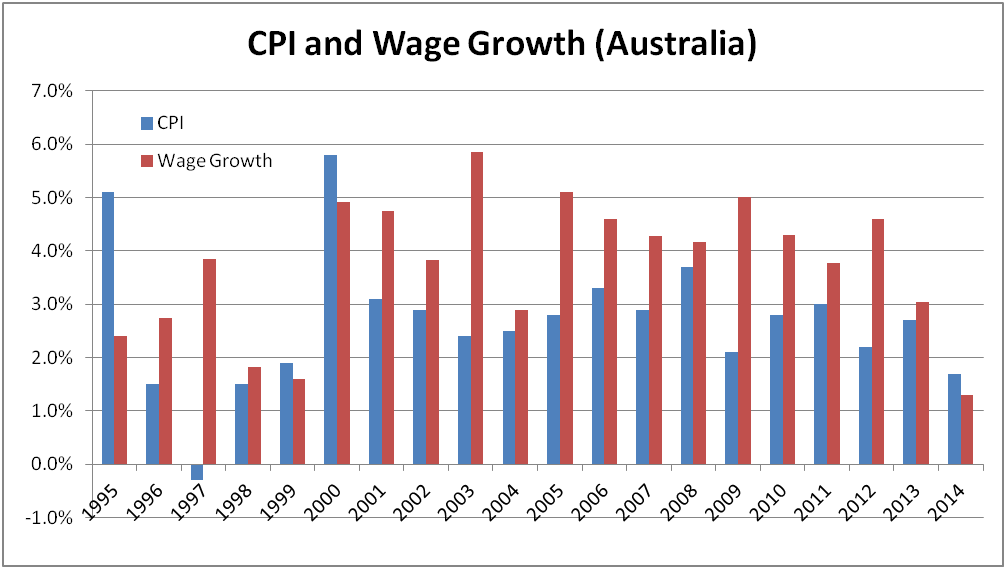
The unemployment rate is well-covered by mainstream media. What is less well-known is that real wage growth in Australia is negative. The purchasing power of Australian wages is heading backwards, and part-time workers are being squeezed particularly hard.
Negative real wage growth is reasonably rare in Australia. The chart below, which plots annual wage growth and inflation, shows that the last time that inflation exceeded wage growth was in 2000.
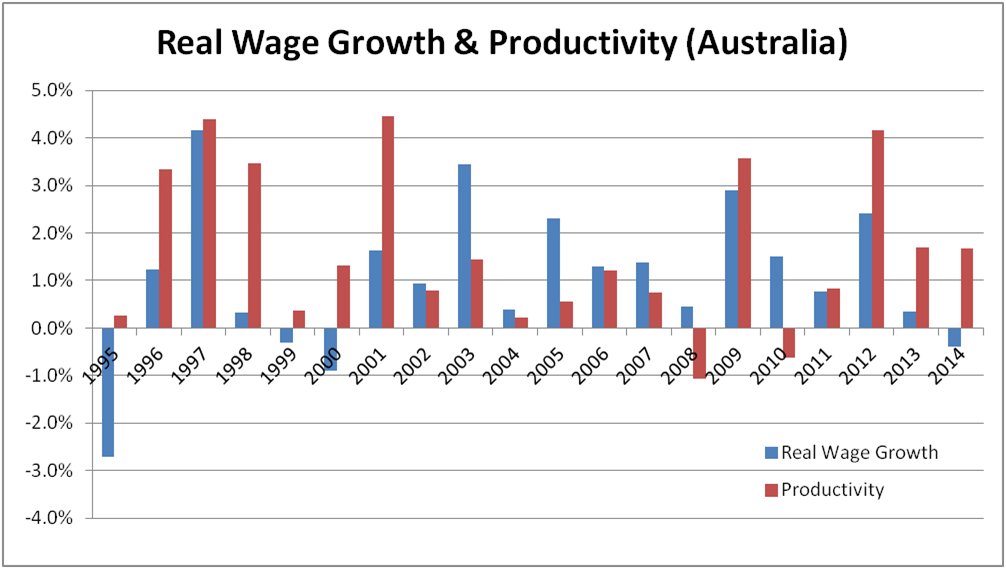
Also of note is that productivity remains at fair levels relative to history. It’s reasonable to expect that workers would at least participate in some of the benefits of productivity via wage growth, although the relationship is pretty loose, as shown in the chart below. The last three years are a story of workers experiencing little participation in the productivity gains that have been derived, adding further detail to the story of labour market softness.
How do soft labour markets affect retirement outcomes?
To understand the impact of soft labour market conditions on retirement outcomes we need to consider both the micro and the macro effects.
Micro perspectives take account of the individual, including:
- Risk of unemployment resulting in no employer contributions, no voluntary contributions and a drawdown in savings and even an increase in debt to fund life’s necessities
- Lower real wages which mean a reduced propensity to save
- Lower age pension payments than expected, as increases in the age pension are currently indexed to the maximum of inflation, wage growth and a measure of inflation of a pensioner’s likely goods and services (wage growth would generally be expected to be the highest of these three in a normal environment). At the time of writing, the government’s proposal to drop wage indexation looks like it will be rejected by the senate.
However we should also consider the macro perspectives as well. Here a longer term environment of soft labour market conditions could also have important impacts:
- Lower savings levels and so greater reliance on the age pension by the population
- A lower than forecast payment level (due to indexation being lower than expected)
- A weakened federal budget position (all else equal) due to lower income tax revenues and greater unemployment benefits.
Note that the first point above has a negative impact on the budget while the second point has a positive impact.
We have seen that the economic environment does not always align with the market environment (something Ashley Owen’s articles make clear). However we can see that there is more to retirement outcomes than just market returns, with a range of economic variables affecting retirement outcomes. The soft labour market is one such factor, and in this case it has largely negative effects at both a micro and macro level. Let’s hope that new sources of economic growth will soon emerge in Australia.
David Bell is Chief Investment Officer at AUSCOAL Super. He is working towards a PhD at University of New South Wales.